What are Terpenes?

Written by Georgia Chappell & Reviewed by Paul Holmes.
What are Terpenes? The Taste and Smell of Cannabis
Have you ever wondered, ‘what are terpenes’? These natural sensory experiences are what give all of our favourite scents their unique flavour profile. They’re the reason why lemons are citrusy, why forests are thick with the aroma of pine, or why essential oils hold such pleasant pungency. We have terpenes to thank for all of this natural beauty.
Keep reading for all the information you need on ‘what are terpenes’
What are Terpenes?
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, the essential oils which create all plants’ unique odours and flavours.1 In practical terms, these plant compounds are there to either attract or repel other organisms. And unsurprisingly, whether the intended terpene was to attract pollinators or ensure its survival, we can’t get enough of them. 2
Around 140 chemicals and compounds found in the cannabis strains we know and love belong to these aromatic, organic hydrocarbons – offering a wide and varied sensory profile which are unique and often complementary.3
Terpenes vs Terpenoids
Terpenes are organic compounds found in plants that contribute to their aroma and flavour. They are composed of repeating units of isoprene and are typically volatile.
Terpenoids, on the other hand, are terpenes that have undergone a chemical modification, often through oxidation or rearrangement. This alteration can occur naturally within the plant or through processes like drying and curing.
While terpenes are hydrocarbons, terpenoids contain additional functional groups like oxygen. Essentially, terpenoids encompass a broader range of compounds due to their modified structure, including both terpenes and their derivatives.

Are Terpenes safe for consumption?
Yes, Terpenes are generally safe for consumption when used in appropriate amounts, but it's important to consider individual sensitivities and potential allergic reactions. Speak with your doctor if you may have any concerns about terpenes.
Do terpenes get you high?
While terpenes aren’t intoxicating, some believe they may impact the effects of THC, the cannabinoid responsible for the high feeling of cannabis.
Terpenes can also have many potential effects on the body. For example, a 2020 study discovered that some terpenes such as Limonene, may have the potential to eventually benefit certain mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder.
Do terpenes have an intoxicating effect?
Terpenes themselves do not have intoxicating effects, but they can modulate the effects of cannabinoids like THC. Their synergistic action with cannabinoids can influence the overall cannabis experience. A few key points are:
- Terpenes enhance or mitigate the effects of cannabinoids.
- They contribute to the entourage effect, altering the psychoactive experience.
- Terpenes alone do not produce intoxication.

Types of Terpenes
Terpenes are vital to our identification and appreciation of fruits, vegetables, and spices, and fundamental to the careful construction of CBD oils from the cannabis plant. Terpenes in this amazing plant are made in sticky resin glands where CBD and other cannabinoids are produced.
There are many different types of terpenes. Here are some of the most important terpenes found in the cannabis plant which are used around the world for their various therapeutic effects:
- Limestone
- Pinene
- Myrcene
- Linalool
- Beta-Caryophyllene

1. Limestone
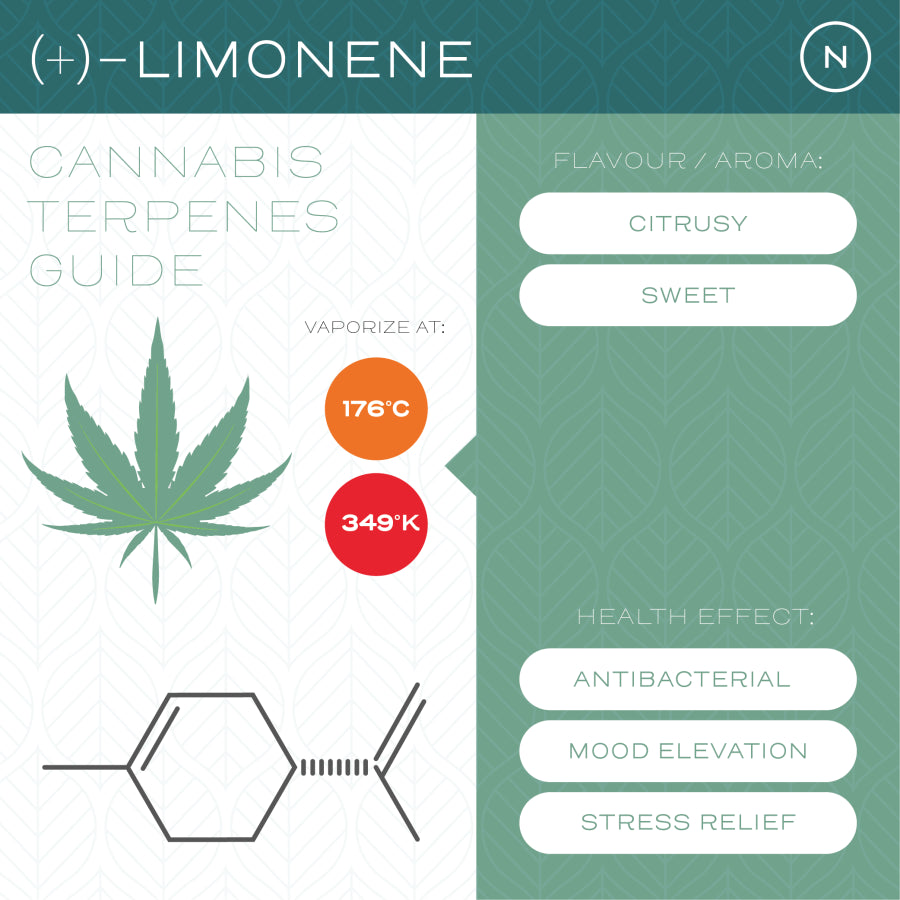
Limonene (pronounced “li-muh-neen”) is found in the aroma of oranges, lemons, limes, and all things citrusy. Whether it’s citrus rind, juniper, rosemary or peppermint, this pleasant smell is attributed to an elevation in mood and spirit.
Limonene – with its alluring scent – is present in many of the products we use today, and research has been conducted to explore how it may be used to tackle obesity and inflammation.
2. Pinene

The earthy, woody smell of pinene is typically found in the bark resin of pine and fir trees. One of the most abundant terpenes in nature, it has begun to be used in medicine as an anti-inflammatory, expectorant, bronchodilator and local antiseptic.
Although evidence is limited, studies suggest that pinene also has anxiolytic (anxiety-relieving), antidepressant and anti-seizure properties, and it may even be effective in the treatment of chronic neurological conditions, such as chronic pain.
3. Myrcene

The citrus and herbal smell attributed to thyme, bay leaves, hops and the sweet mango all come from the most common terpene found in cannabis – myrcene. Hailed for an array of medicinal benefits, including its prevention of peptic ulcer disease, this incredible terpene plays a vital role in the world of CBD.
A popular flavouring and aroma agent in food and beverages, myrcene has been shown to have antioxidant, anti-aging and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as the potential to relieve pain and anxiety.
4. Linalool

Known for its calming and relaxing effects, the floral spice found in lavender, birch and rosewood is a result of linalool’s complex chemistry. Studies explore the many ways this terpene can boost our immune system, significantly reduce cigarette-induced lung inflammation, and aid in the restoration of the neurological and behavioural impairments associated with Alzheimer’s.
While more clinical trials are needed, there’s evidence to suggest that linalool can be just as effective as commercial anti-anxiety, analgesic and anti-depressant medications (such as lorazepam, benzodiazepam and paroxetine), often with a lower adverse effects profile.
5. Beta-Caryophyllene

Found in peppercorns, cloves, basil and cotton, beta-caryophyllene is noted for its peppery and spicy scent. Like many others, there are interesting studies surrounding this terpene which make it an attractive component of many high-quality CBD oils.
For instance, the oral combination of phytocannabinoids and beta-caryophyllene appears to be promising for the treatment of chronic pain due to their high safety and low adverse effects profiles. Furthermore, black pepper oil, of which beta-caryophyllene is the main component, is found to possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive properties.
Terpenes and CBD
After methane, terpenes are the most common volatile organic compound found in the atmosphere. Put simply, they are everywhere. And like all things in nature, terpenes naturally interact with their chemical environment. In CBD oil, that’s the cannabinoids and other chemical compounds found in cannabis, and this means that they ultimately influence how we benefit from this herbal synergy.
It has been observed that terpenes “display unique therapeutic effects that may contribute meaningfully to the entourage effects of cannabis-based medicinal extracts”. The “entourage effect” is based on the hypothesis that the various compounds found in cannabis extracts, including terpenes and cannabinoids, can work together to enhance the extract’s effectiveness.

Harnessing the power of terpenes
At Naturecan, we harness the power of terpenes by putting our broad-spectrum CBD through a complex extraction and purification process. This allows our products to retain vital hemp compounds (including CBD, certain terpenes and other phytochemicals) while removing THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and other impurities – ensuring product safety and quality, while maximising the potential benefits of the entourage effect. Here’s a brief overview of this three-step process:
1. CO2 Extraction
In step one, pressurized carbon dioxide is passed through the hemp plant in order to strip away the desired CBD compounds and other phytochemicals. This creates a safe, clean and high quality CBD concentrate (or crude oil).
2. Chromatography
In step two, we use Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC), an advanced purification system developed by RotaChrom, to remove as much THC as possible. This produces a concentrated output with non-detectable levels of THC (0.01%).
3. Distillation
In the final step, we further refine the concentrate by distillation. This process allows the oil to retain certain terpenes, minor cannabinoids and other phytochemicals, while removing any compounds (such as lipids, waxes, flavonoids and chlorophyll) which may negatively affect the taste, consistency or purity of the end product. The distilled oil contains 90-95% CBD and at least 5% other minor cannabinoids, such as CBG, CBC, and CBDA. This rich mix of additional cannabinoids and terpenes helps to create oil of the highest purity and quality.
Terpenes FAQs
How do Terpenes differ from essential oils?
Terpenes are distinct from essential oils in that they are organic compounds found in plants responsible for aroma and flavour, while essential oils are concentrated extracts derived from plant material containing various compounds, including terpenes.
What role do Terpenes play in aromatherapy?
In aromatherapy, terpenes play a significant role by emitting aromatic compounds that can evoke specific therapeutic effects, such as relaxation, stress relief, or improved mood.
Can Terpenes help with sleep or anxiety?
Certain terpenes, like myrcene and linalool, are believed to have potential benefits for sleep and anxiety due to their calming and sedative properties. However more research is needed to fully understand their efficacy.
How are Terpenes extracted from plants?
Terpenes can be extracted from plants through methods like steam distillation, cold pressing, or solvent extraction, depending on the plant and desired terpene profile.
For more on our extraction process, read our blog right now.
Are there specific Terpenes that are beneficial for skin care?
Yes, certain terpenes like limonene and linalool are known for their beneficial effects in skincare, such as anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
Check out our CBD Skincare to upgrade your beauty routine with terpenes today.
How do environmental factors affect Terpene production in plants?
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and soil composition can significantly affect terpene production in plants, influencing both the type and quantity of terpenes produced.
Can Terpenes be synthesised artificially, and how do these compare to natural Terpenes?
Yes, terpenes can be synthesised artificially, but synthetic terpenes may not always replicate the exact composition or effects of natural terpenes found in plants. Natural terpenes often contain additional compounds and isomer variations that contribute to their therapeutic properties.
References:
1. Eberhard Breitmaier (2006). Terpenes: Flavors, Fragrances, Pharmaca, Pheromones. Wiley-VCH
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC167096/
- https://www.medicaljane.com/category/cannabis-classroom/terpenes
- https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1105/limonene
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23838456/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28260017/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/pinene
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.583211/full
- http://www.aromaticscience.com/the-effect-of-a-minor-constituent-of-essential-oil-from-citrus-aurantium-the-role-of-β-myrcene-in-preventing-peptic-ulcer-disease/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8326332/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/linalool
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567576915301089
- http://europepmc.org/article/med/26549854
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.583211/full
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3820295/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261591338_Antioxidant_Anti-inflammatory_and_Antinociceptive_Properties_of_Black_Pepper_Essential_Oil_Piper_nigrum_Linn
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemical-engineering/terpene
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21749363/




