What are cannabinoids? And how do they work?

Written by Thomas Wrona and reviewed by our qualified expert, Moyra Cosgrove, Head of Nutrition at Naturecan, SENR Registered Nutritionist and DProf candidate at LJMU
Summary
- Cannabinoids are the active ingredients that make broad spectrum CBD oil tick
- Cannabinoids work within your body’s endocannabinoid system, providing balance-based benefits in the process
- The easiest way to benefit from cannabinoids is by taking broad spectrum CBD or CBG products
Are you wondering what makes broad spectrum hemp so powerful...what’s enabled it to positively impact so many people?
If so, we’ve got the answer: cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are the catalyst that makes hemp able to do all the great things it does! Keep reading to learn about these mysterious compounds — hopefully they won’t seem too mysterious anymore after we’re through.
Cannabinoids 101
What are cannabinoids? To put it as simply as possible, they’re active ingredients within hemp and cannabis plants.
Cannabinoids are fat-soluble molecules (similar to vitamin A or D) that are good for both the plants that produce them and for us. They were first discovered in the early 1900s.
You can probably guess why they were named what they were — cannabinoids were first identified in a sample of resinous hash from the cannabis Sativa plant.
Pioneering chemist Roger Adams discovered the cannabinoid CBD (cannabidiol) in his US lab in 1940, while cannabis research godfather Raphael Mechoulam discovered THC at the Hebrew University of Israel in 1964.
Interestingly enough, it wouldn’t be until the 1990s that researchers finally discovered how cannabinoids worked. But more on that later — this is cannabinoids 101, after all.

How many cannabinoids are there?
Cannabis and hemp produce over 100 cannabinoids between the two of them. At last check, there were roughly 140 identified cannabinoids. Below are some of the top ones:
- CBD (cannabidiol)
- THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
- CBG (cannabigerol)
- CBC (cannabichromene)
- CBN (cannabinol)
- CBT (cannabitracin)
- CBL (cannabicyclol)
Making matters even more complex, cannabinoids can exist in at least three different forms, which chemists call isomers. First up is the ‘raw’ form, which hasn’t been heat-activated:
- CBDa (cannabidiolic acid)
- THCa (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid)
- CBGa (cannabigerolic acid)
- CBCa (cannabichromenic acid)
- CBNa (cannabinolic acid)
Then the ‘standard’ form we listed at first, then yet another class of unique isomers:
- CBDv (cannabidivarin)
- CBDva (cannabidivarinic acid)
- Delta-8 THC (delta-8 tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Delta-10 THC (delta-10 tetrahydrocannabinol)
- THCv (tetrahydrocannabivarin)
- THCva (tetrahydrocannabivarinaric acid)
- CBGva (cannabigerovarinic acid)
- CBCv (cannabichromevarin)
Talk about acronym soup! But don’t feel too overwhelmed. Regardless of which category any given cannabinoid falls into, virtually all natural cannabinoids are really good at doing one thing: promoting inner-body balance.
How medical cannabinoids work
What are medical cannabinoids? Technically speaking they’re any cannabinoid that’s used for medical purposes. Any and all-natural cannabinoids can become medical when they’re used for the proper dose.
In other words, the qualifying conditions for medical cannabinoids can and do vary from person to person. Most people find the cannabinoid CBD (cannabidiol) most medicinal, yet in recent years there’s been growing interest in the medical potential of ‘trace cannabinoids’ like CBDa, delta-8 THC, and THCv. Some people even find that the highly psychoactive cannabinoid delta-9 is most medicinal for them.

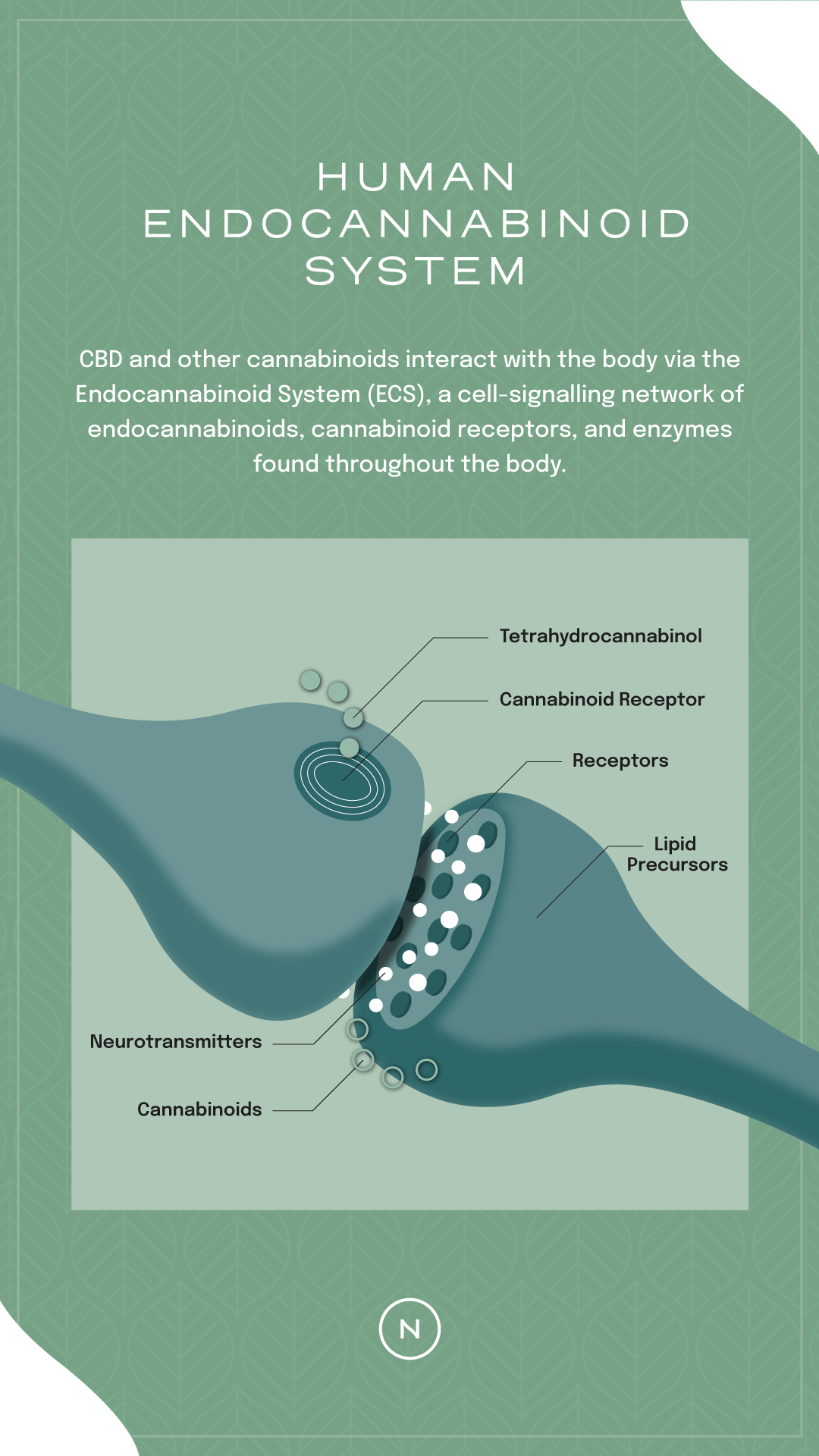
The way cannabinoids work has baffled scientists for over a century. As we said above, a big breakthrough came in the 1990s — that’s when biochemists discovered something called the human endocannabinoid system. This system is built into the bodies of every human being (in fact, every mammalian species, and other species too).
What does the endocannabinoid system do? In the words of chemist Vincenzo Di Marzo, it promotes eating, sleeping, relaxation, and forgetting. The endocannabinoid system helps your body become more balanced and dynamic all at once. And it does this by sending vital feedback signals to other parts of your body, much like a car’s dashboard provides vital info about the state and speed of the vehicle.
Here’s what’s really fascinating: your endocannabinoid system receives feedback from two totally different types of cannabinoids. In addition to the cannabis-derived cannabinoids we’ve mentioned so far, your system produces large amounts of its own cannabinoids, too. These two types are called phytocannabinoids (plant cannabinoids) and endocannabinoids (internally-made cannabinoids).
The fact that your body already produces substances like the ones contained in cannabis and hemp helps explain why these plants work so well — and why they’re so free of harmful side effects. It’s hard to name another class of substances (even natural substances) that are so well tolerated. Your body produces none of its own caffeine, which explains why caffeine’s energizing properties come with jitters and proceeding withdrawals. And your body produces only trace amounts of alcohol, which explains why overdoing the alcohol leads to serious, sometimes life-threatening side effects.
Hemp and its cannabinoids are different. Your body produces endocannabinoids for all sorts of reasons...everywhere...all the time. Add phytocannabinoids like CBD into the mix and things stand to get even better. According to professor Bob Molamede, cannabinoids are what make the complexity of human life possible. Without the feedback loops they facilitate, we probably wouldn’t have made it as far as we’ve come. Cannabinoids make us flexible and creative enough to envision — and then create — a better future. And that concept holds true on the microcosmic personal level, as well as the macro.
Let’s get a little more specific. The moment you take CBD or THC, they begin to bind to special endocannabinoid receptors located throughout your body and mind. Different cannabinoids bind to different receptors:
CBD binds to CB2 receptors located throughout your muscles, mitochondria, and digestive tract, promoting balance without causing psychotropic mental effects.
THC binds to CB1 receptors located throughout the brain and other parts of the central nervous system, causing euphoria and full-body relaxation.
CBG binds to serotonergic receptors located within the brain, fostering mental balance in a nuanced way. In the peripheral body, CBG may have unique anti-microbial effects.
CBDa binds to serotonergic receptors located within the body, providing a type of indirect mental balance that could keep you confident and calm.
The unique way cannabinoids work together
As great as the specialised benefits mentioned above may be, cannabinoids get even better when they’re taken together. It’s kind of like the healthfulness of citrus fruits can’t be fully explained by vitamin C. Nope, it’s thanks to the unique combination of antioxidants and flavonoids contained within, of which vitamin C is just a small part! Broad spectrum hemp oil that’s rich in CBD, CBG, and other cannabinoids is the same way. It’s much, much more powerful than any of these ingredients alone.
It’s actually even more powerful than the sum of their parts. Research from Israel’s leading cannabinoid lab hints that only about one-quarter of broad spectrum hemp oil’s power comes from CBD itself. The other three-quarters come from other cannabinoids and terpenes — and the ways in which they synergise.
How do cannabinoids work alongside terpenes? Interestingly enough, the terpenes in hemp activate many of the same receptors that cannabinoids do. A spicey terpene called beta-caryophyllene does this so directly that researchers have deemed it the first dietary cannabinoid that doesn’t come from cannabis. Terpenes may even help open up barriers within the brain, allowing greater amounts of cannabinoids to pour in and do what they do best.
This type of cannabinoid + cannabinoid and terpene + terpene synergy is called the entourage effect...and it doesn’t just apply to CBD oil. It applies CBG oil and CBN oil, too!
Natural cannabinoids vs. synthetic cannabinoids
What are cannabinoids? We’ve already established that one form of cannabinoids (phytocannabinoids) serves as the active ingredients within cannabis/hemp, while a second form of cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) provides an internal checks-and-balances system within your body.
But there’s a third class of cannabinoids you should know about: synthetic cannabinoids. These cannabinoids were first created by researchers in their quest to better understand the endocannabinoid system. More controversially, synthetic cannabinoids make for great pharmaceutical drugs because they can’t be patented.
While synthetic cannabinoids are often better than no cannabinoids, their unnatural nature means they can have weird and unusual side effects. Early research involving these synthetics put a bad rap on cannabis because they occasionally made lab rats and early clinical subjects insane. More recently, a French study involving synthetic cannabinoids was stopped when its test subjects began dying.
These types of tragedies come with a painful learning lesson: if you’re going to mess with something that activates the endocannabinoid system, it should probably be natural. Natural cannabinoids like CBD and CBG are incredibly safe and impossible for humans to ‘overdose’ on. Why? Because endocannabinoid receptors aren’t present in the parts of your brain responsible for controlling vital processes like breathing!
The easiest (and best!) ways to use cannabinoids
So, what are cannabinoids? They might just be the best compounds available if you wish to naturally boost your health! They’re also great for athletes. World’s Strongest Man-turned celebrity boxer Eddie Hall calls CBD a “secret weapon” when it comes to recovering from hard workouts — and for good reason. Are you ready to experience the benefits of cannabinoids for yourself? If so, there are two major types of cannabinoid products you should know about:
- Ingestible products like oils, tinctures, and edibles
- Topical products like creams and salves
CBD ingestibles
Ingestible cannabinoid products are a pretty diverse bunch. First and foremost, there’s the CBD oil/tincture: a simple product which features hemp extract within an oily base. (You can read more about CBD oil and its effects here.)
And CBD oil is just the start. Other ingestibles include CBD edibles, capsules, and CBD-infused beverages. (Side note: you can make these beverages yourself by placing a few drops of CBD oil into coffee or tea!)


CBD topicals
CBD topicals are the second primary type of cannabinoid product. While topicals aren’t as powerful as ingestibles in the sense that they don’t get absorbed into your bloodstream, research nonetheless shows that topical cannabinoids may have some impressive skin-centric benefits.
Athletes can use CBD cream to soothe their muscle soreness, while all you skincare enthusiasts out there can use CBD skincare products to get your glow up. Many users report that topical CBD calms down ‘angry’ skin and sets the stage for their skin to truly shine. Check out our dedicated article on CBD skincare to get more info on this topic.
What are cannabinoids? Summing things up
What are cannabinoids? Besides being interesting, unusual, and amazing, they’re the active ingredients behind all those hempy benefits we’ve come to know and love!
Cannabinoids work their magic by working with a physiological system your body is already using — and that’s part of what makes them so powerful. You’d be hard-pressed to find another natural substance that exerts the variety of effects that cannabinoids do.
If you’re ready to feel the power of cannabinoid-infused products for yourself, take a visit to our online shop today.
References
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja01858a058
- https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/list-major-cannabinoids-cannabis-effects
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3951193/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19630737/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19999796/#:~:text=When%20administered%20in%20high%20doses,miscarriage%20and%20intrauterine%20growth%20retardation
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17828291/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17828291/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33168643/
- https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/cbda-proves-to-be-a-star-ingredient-of-cbd-301072619.html#:~:text=A%20Canadian%20study%20in%202013,effective%20treatment%20for%20chemotherapy%20patients
- https://www.projectcbd.org/science/pure-cbd-better
- https://www.pnas.org/content/105/26/9099
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31481004/
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-35337671
- https://www.theweek.co.uk/99068/what-is-cbd-oil
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30993303/



